Spring Cloud Gateway security with JWT
Spring Cloud Gateway provides a powerful way to handle HTTP traffic between microservices. It also provides several mechanisms for securing the gateway, including JWT.
In this blog post, we will explore how to use Spring Cloud Gateway with JWT for securing microservices.
What is JWT ?
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are a popular way of securely transmitting information between parties. A JWT is a string that consists of three parts: a header, a payload, and a signature. The header contains metadata about the JWT such as the type of token and the cryptographic algorithm used to sign it. The payload contains the data that is being transmitted, such as user information or authorization data. The signature is used to verify that the JWT has not been tampered with.
JWTs are often used in web applications to securely transmit user information or authorization data between the client and server. They can also be used to secure communication between microservices.
How to use JWT with Spring Cloud Gateway ?
Spring Cloud Gateway provides a powerful way to handle HTTP traffic between microservices. It also provides several mechanisms for securing the gateway, including JWT.
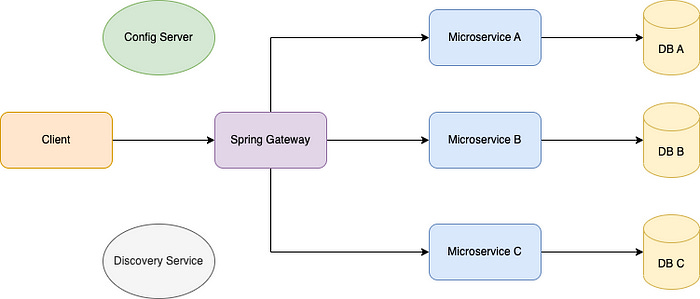
Lets take an example,
Here we have the Spring Gateway module that accept all incoming requests from client and here we do the authentication and authorization part and if successful gateway will redirect the traffic to relevant Microservice.
Now lets dive in Gateway code to see what is going on there,
First of all, we need the filter itself, which will be checking all the incoming requests to our API.
package com.rd.spring.gateway.config;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilter;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@RefreshScope
@Component
public class AuthenticationFilter implements GatewayFilter {
private final RouterValidator routerValidator;
private final JwtUtil jwtUtil;
@Autowired
public AuthenticationFilter(RouterValidator routerValidator, JwtUtil jwtUtil) {
this.routerValidator = routerValidator;
this.jwtUtil = jwtUtil;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
if (routerValidator.isSecured.test(request)) {
if (this.isAuthMissing(request)) {
return this.onError(exchange, HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
}
final String token = this.getAuthHeader(request);
if (jwtUtil.isInvalid(token)) {
return this.onError(exchange, HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN);
}
this.updateRequest(exchange, token);
}
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
private Mono<Void> onError(ServerWebExchange exchange, HttpStatus httpStatus) {
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
response.setStatusCode(httpStatus);
return response.setComplete();
}
private String getAuthHeader(ServerHttpRequest request) {
return request.getHeaders().getOrEmpty("Authorization").get(0);
}
private boolean isAuthMissing(ServerHttpRequest request) {
return !request.getHeaders().containsKey("Authorization");
}
private void updateRequest(ServerWebExchange exchange, String token) {
Claims claims = jwtUtil.getAllClaimsFromToken(token);
exchange.getRequest().mutate()
.header("email", String.valueOf(claims.get("email")))
.build();
}
}In the filter we defined that we have some secured routes and some resources that do not require JWT.
If the resource is made to the secured route, then we check the validity of JWT
If all these conditions are true, we add extract email from the JWT and add that as a new header. So all the sub sequent calls can directly get the email from the header without decoding JWT.
Now lets check how routes are configured,
package com.rd.spring.gateway.config;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.RouteLocatorBuilder;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.hystrix.EnableHystrix;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableHystrix
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class GatewayConfig {
private final AuthenticationFilter filter;
@Bean
public RouteLocator routes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("cars-service", r -> r.path("/cars/**")
.filters(f -> f.filter(filter))
.uri("lb://cars-service"))
.route("auth-service", r -> r.path("/auth/**")
.filters(f -> f.filter(filter))
.uri("lb://auth-service"))
.build();
}
}All the request that starts with
/carsshould route to cars-service.All the request that starts with
/authshould route to auth-service.
Now lets check how RouterValidator looks like,
package com.rd.spring.gateway.config;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
@Component
public class RouterValidator {
public static final List<String> openApiEndpoints = List.of(
"/auth/register"
);
public Predicate<ServerHttpRequest> isSecured =
request -> openApiEndpoints
.stream()
.noneMatch(uri -> request.getURI().getPath().contains(uri));
}Only
/auth/registerdefined as an open endpoint.
In summery,
AuthenticationFilter will be applied to all requests except
/auth/register.If a request is made to a secured resource without proper authorization, then Gateway will reject it.
If a request is made to a secured resource with proper authorization, then Gateway validate the JWT, extract email and mutate request by adding the new email header and finally redirect request to relevant microservice.
You can find the repo here — https://github.com/rajithd/spring-cloud-security-jwt
Lets test this now,
Clone the project and build all microservices,
./gradlew clean buildNow start all the microservices one by one,
java -jar config-service/build/libs/config-service-0.0.1.jar
java -jar discovery-service/build/libs/discovery-service-0.0.1.jar
java -jar gateway-service/build/libs/gateway-service-0.0.1.jar
java -jar auth-service/build/libs/auth-service-0.0.1.jar
java -jar cars-service/build/libs/cars-service-0.0.1.jarLets send a request to a secured resource without authorization header,
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8080/cars'Response will be 401
Now lets try to get proper access token,
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/auth/register' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"email": "a@a.com",
"password": "password",
"name": "name"
}'{
"accessToken": "<TOKEN>",
"refreshToken": "<TOKEN>"
}Then lets send the another request to cars endpoint with proper header.
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8080/cars' \
--header 'Authorization: <TOKEN>'[
{
"carId": "1",
"carName": "Audi"
}
]There are several ways we can enhance this solutions.
Introduce IDP like KeyCloak.
AWS Deployment using EKS, EB or Fargate.
I will be working on these enhancement in future so you can expect more articles around this code.
Thanks for reading.